compression test discraction test|cervical compression test vs spurling's : distribute If pain is relieved as a result of the movement, then the test is positive for nerve root compression and facet joint pressure. The grade of the pressure would be determined by the amount of pressure and pain relieved while performing the test. Reset Password . Soundgasm.net Logo Home Login Signu.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Moja ČSOB - csob.sk je vaša vstupná brána do elektronického bankovníctva ČSOB. S Moja ČSOB môžete mať prehľad o vašich financiách, platiť účty, nastavovať si služby a .
If pain is relieved as a result of the movement, then the test is positive for nerve root compression and facet joint pressure. The grade of the pressure would be determined by the amount of pressure and pain relieved while performing the test."Cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from .The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and .Gaenslen's Test (Gaenslen's maneuver) is one of the five provocation tests that can .
SIJ Compression/Distraction Test. Purpose: To assess for sacroiliac contributions to the patient's symptoms. SIJ Compression/Distraction are often separated into two different tests. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: .Gaenslen's Test (Gaenslen's maneuver) is one of the five provocation tests that can be used to detect musculoskeletal abnormalities and primary-chronic inflammation of the lumbar .
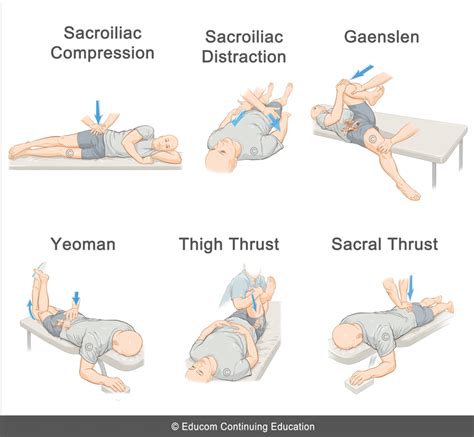
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with hip .In this article we will review the SIJ provocative tests involved with diagnosing SIJ pain. Laslett et al (1, 2) describes five SIJ provocative tests: 1) Distraction 2) Thigh Thrust 3) Compression 4) .
compression tester bleeding to zero all the time
Distraction test. Differentiates between radicular pain in the back of the neck, shoulder, and arm and ligamentous or muscular pain in these regions. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner grasps the patient's .
Test Clusters for Diagnosis of Radicular Syndromes One study of mild to moderate C6-C7 radicular syndromes (based on EMG and nerve conduction studies) has suggested that the . The neck distraction test is performed with the patient in a supine position. The examiner places one hand under the patient's chin and the other hand around the occiput, . What is the Spurling test? The Spurling test is a physical assessment to diagnose cervical radiculopathy or a pinched nerve in your neck. If you experience neck pain, a healthcare provider may offer this test.The Spurling test can tell your provider if something is squeezing or pressing against a nerve (nerve root compression) in your cervical spine.
Purpose: The Apley Compression test or Apley Grind test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus.. How to Perform the Apley Compression Test. Position of Patient: The patient should be positioned in .
• Cervical Flexion Rotation Test • Cervical Compression, Jackson’s Compression, Maximum Foraminal . traction (cervical distraction) test, and Arm Squeeze test may be used to increase the likelihood . Cervical Orthopedic Tests Page 6 of 30 of a cervical radiculopathy, whereas a negative outcome of combined Upper Limb Neural . The Apley grind test, also known as the Apley compression test or the Apley test, is a maneuver performed to evaluate meniscus injury. Clinicians usually perform it in conjunction with the Apley distraction test, which assesses for ligamentous injury. Meniscal injuries are very common and are associated with significant pain and morbidity. Foraminal compression test to assess for a space occupying condition of the cervical spine. (A) The therapist places downward pressure on the client’s head while the client’s neck and head are in a neutral position. . Cervical Distraction Test. The (cervical) distraction test, like the foraminal compression test, is performed to assess a .
The test has also been referred to as the Foraminal Compression Test, Neck Compression Test, or Quadrant Test. The Spurling test is considered a provocative test used in the spinal examination. . Neck Distraction test: Active distractive force is applied by examiner while grasping patient’s head under the occiput and chin. A positive test . SI distraction test. with the patient supine on the examination table a posteriorly directed force over the ASIS. test is considered positive when pain is reproduced in the SI joint. . limits the motion and shear forces across the SI joint . You might see it referred to as an Apley grind test or an Apley compression test. Providers use these names interchangeably to refer to the same test. Advertisement. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.
Purpose: To assess for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Test Position: Sitting. Performing the Test: With the patient's arm in supination, the examiner applies pressure with his/her thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. This is located just distal to the wrist crease. A positive test occurs when the patient complains numbness and tingling in the median nerve distribution .
Because the thigh thrust and distraction tests have the highest individual sensitivity and specificity, respectively, performance of these tests first may be optimal. If both tests provoke familiar pain, no further testing is indicated. If one test is positive, the compression test is applied and if positive, aLaslett et al further investigated the diagnostic power of pain provocation sacroiliac joint (SIJ) tests individually and in various combinations, in relation to a diagnostic injection. The tests employed in this study were: distraction, right sided thigh thrust, right sided Gaenslen's test, compression, and sacral thrust.
Slightly flex the patient’s neck and pull the head towards your torso, applying a distraction force. A positive test is when the patient’s symptoms are reduced with the traction. Diagnostic Accuracy: Specificity: .90; Sensitivity: .44; -LR: .62; +LR: 4.4 (“Reliability and diagnostic accuracy of the clinical examination and patient self .Learn how to administer the five provocative tests used in diagnosis of the SI joint: FABER, Compression, Thigh Thrust, Distraction, and Gaenslen. Patients; Providers; Investors; Patient Overview Diagnosis Overview; Symptoms; Diagnostic Tests . While 1 positive test raises suspicion, 3 or more positive tests would indicate the SI joint as a .
The Cervical Distraction Test also called Traction/Distraction test is a symptom-relief test to assess for cervical radicular syndrome/cervical radiculopathy. It has been described to have a sensitivity of 44% and a high specificity ranging between 90 to 97% in the review of Rubenstein et al. (2007). It therefore, has a moderate clinical value .Purpose of Test: To identify the effect of vertebral compression to the patient’s symptoms. Test Position: Sitting. Performing the Test: Apply an inferiorly directed pressure through the superior aspects of both shoulders. A positive response is an indication of pain. Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown. Importance of Test: With a reproduction of pain, it could signal tissue trauma, .
tests for sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Purpose: To assess the mobility and laxity of the hip joint. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: With the patient's hip passively placed in 30 degrees of hip flexion, 30 degrees of abduction, and 15 degrees of lateral rotation, the .Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a labral tear or acromioclavicular lesion. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is instructed to place the shoulder into 90 degrees of flexion and 10 degrees of adduction. Next, the arm is actively internally rotated so the thumb is pointing downward. The instructor then applies a inferior directed force (into .Distraction test; Compression test; Thigh thrust test; Gaenslen’s test; Sacral thrust test; Laslett et al (2005) state that no further examination is wishful if both distraction and thigh thrust test provoke familiar pain. If only one test or 2 other tests are positive, further testing is required to obtain a valid result. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
compression tester blue
Special Test: Apley’s Compression Test: PROCEDURE: • Patient is prone. • Patient then flexes affected knee to 90° • Therapist’s one hand grasps patient’s heel and ankle while the other hand stabilizes the leg.
The neck distraction test is performed with the patient in a supine position. The examiner places one hand under the patient's chin and the other hand around the occiput, while simultaneously .Thoracic Distraction (Decompression) Test. Purpose of Test: To identify the impact decompression has on the patient’s symptoms. Test Position: Long sitting. Performing the Test: Patient’s arms are crossed. While kneeling or standing behind patient, slip your hands beneath patient’s axillary areas to grasp the patient’s forearms. Lean .To perform the TFCC Compression Test according to Prosser et al. in the year 2011, fixate your patient’s radius and ulna with one hand close to the joint line. Then grab your patient’s hand at the height of the meta-carpals from radial and bring his wrist .
si distraction test positive
Compression Test, Shoulder Abduction (Re-lief) Test, Neck Distraction Test, L’hermitte’s Sign, Hoffmann’s Sign and Adson’s Test. This review describes some specialized provocative tests with comprehensive litera-ture review. The goal of this review is to de-velop standardization in the performance and clinical use of these tests. Each .
Gismervik et al. in the year 2017 performed a rigorous meta-analysis of shoulder tests for SLAP lesions and found the Compression-Rotation Test to be the most accurate test with a sensitivity of 43% and a specificity of 89%.
It is our mission to challenge sports and orthopedic physical therapists to become clinical experts by providing residency level education.Follow us! EMAIL:.Purpose: To decide if sacroiliac joint is the source of the patient's symptoms or not. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: Examiner applies a posteroanteriorly directed force to various locations of the sacrum: base, apex, and each side of the sacrum medial to the PSIS (sacral sulcus). Next, the examiner applies a cephalad pressure on the sacrum at each position: base .
positive si compression approximation
web2M Followers, 619 Following, 281 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Catarina Paolino (@catarinapaolino)
compression test discraction test|cervical compression test vs spurling's